Is cannabidiol legal in Switzerland? A burning question with a simple answer: yes. But under what conditions? And what about the European legislations? These are all questions that we will try to answer in this article. But let's start by trying to understand what CBD is and what is its link with the cannabis plant.
What is CBD?
The term CBD refers to the cannabidiol molecule found in the cannabis plant in varying amounts. This molecule is what is called a cannabinoid, a family of active ingredients found in cannabis. There are more than 80 of them, but the most known (and important) are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). Each of these cannabinoids interacts with the CB1 and CB2 neuroreceptors. But where THC can cause a narcotic effect, CBD has no psychotropic impact. Its interaction with the body seems to be limited to therapeutic benefits: painkiller, antidepressant, anticonvulsant, antistress. So many positive effects that justify its popularity on the Swiss and international scenes.
How to consume cannabidiol?
As mentioned above, CBD comes from the cannabis plant. However, it would be simplistic to think that the only way to consume this extract is by smoking. In fact, thanks to the ever-growing success of this substance, a growing number of alternatives have emerged. Here are some of them.
CBD Oil
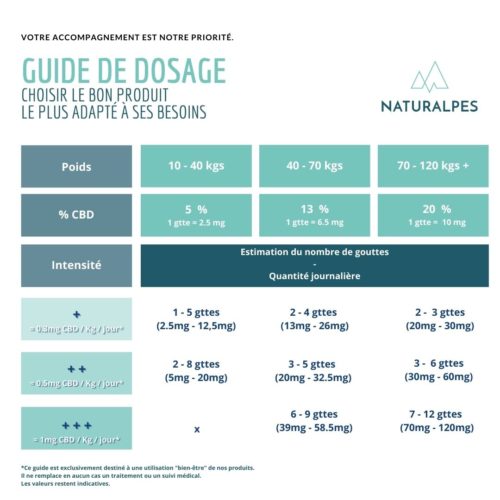
Extracted from dried and crushed cannabis flowers by a very precise process (link to an oil), cannabidiol oil has seduced aficionados and those curious about well-being. How did it work? Its success is largely due to the multitudes of scientific studies that praise its merits:
- Antonio W. Zuardi and his team proved the effectiveness of CBD oil on anxiety by comparing it to a standard anxiolytic available in pharmacies. According to the results of his experiment, an adequate dose of CBD provides an effect equivalent to a drug.
- This other research by Professor Moran Hausman-Kedem highlights the reduction of epileptic seizures in children and adolescents with CBD.
These are just two of many studies on the benefits of CBD oil.
CBD flowers
Flowers are the first image that comes to mind when one thinks of CBD consumption or, more generally, cannabis. But, as already explained above, CBD, unlike THC, does not cause a psychotropic effect. This also applies to dried flowers.
This type of consumption is best reserved for recreational use, for the purpose of relaxation. The use of a vaporiser is recommended. Indeed, it seems to present less of a health risk than the combustion method of consumption.
Other CBD products include relaxing herbal teas and e-liquids.

Cannabidiol and legality
The legislative issues in relation to cannabidiol may seem complex; firstly, because of its link with THC, and secondly, because of the differences in laws between countries.
Cannabis: legal in Switzerland?
Since 2011, according to Swiss law, cannabis containing less than 1% THC is not regulated by the Swiss Drug Law (LStup, SR 812.121).
CBD itself is also not governed by this law because it does not have a psychoactive effect. Moreover, as it has a reputation as a "universal remedy", the cannabidiol content in cannabis and its derivatives is not, for the time being, subject to specific regulation.
This means that as long as a product - whether oil, flower or herbal tea - does not exceed the 1% THC threshold, it is legal, regardless of the CBD content. This is a very interesting law that guarantees consumers a non-psychotropic experience while taking into account the therapeutic benefits that can come from a low dose of THC.
Cannabis: legal in Europe?
To date, there is no European legislation European legislation on cannabis. Each country of the union is responsible for establishing its own laws on the subject. This explains the differences that can be found when crossing the borders. One thing is clear, most of the countries around Switzerland are less tolerant about cannabis. In France, Germany and the United Kingdom, only hemp containing less than 0.2% THC can be cultivated. In Italy, the theoretical limit is also 0.2%, but a margin of error of up to 0.6% THC is tolerated.
Why choose Swiss cannabis?
As we have seen, the comparison between Swiss cannabis and its European cousins is mainly based on the amount of THC allowed. However, a difference of 0.8% can be decisive in the impact of the product. Indeed, a phenomenon called entourage effect can make one cannabis-based solution more or less effective.
The Surrounding Effect
The interaction between the components of a cannabis plant is called the entourage effect.
According to the theory, there are more than 480 components in a cannabis strain. Within these components, three different categories can be found: cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. Each of these three types of components plays an essential role in the consumer's experience: cannabinoids are mainly responsible for physiological effects, terpenes determine taste and smell, while flavonoids are responsible for the colour of the plant.
Two strains of cannabis with different genetics will cause two different effects on the same consumer. Why is this? Precisely because of this entourage effect. The components interact with each other to produce this or that sensation. Each combination has its own particularity. And the more different elements, the more effective.
On the other hand, this entourage effect does not work as well in products containing only a limited number of components. This is why the legal THC dose in Switzerland is more attractive than in its European neighbours.
Legislation on cannabis has changed significantly in recent years. This is partly due to the emergence of various studies on the use of cannabis for therapeutic purposes. However, we are still at the very beginning of this field of research. The various governments are still struggling to establish definitive legislation on the issue. It is therefore to be expected that there will be a number of revisions and updates of Swiss, European or even global laws.

